This guide covers the essential parts of an FTTH/FTTx network using GPON technology, like OLT, ONU, and optical splitters. It also provides easy-to-follow steps for planning, installing, and maintaining these networks to deliver fast internet to homes and
Knowledge base for FTTH/FTTx
network using GPON OLT.
FTTH (Fiber to the home)
is a broadband network architecture that delivers high speed internet, television,
and telephone services directly to end users using optical fiber. Gigabit
Passive Optical Network (GPON) is a widely adopted standard in FTTH networks,
known for its high efficiency and scalability.
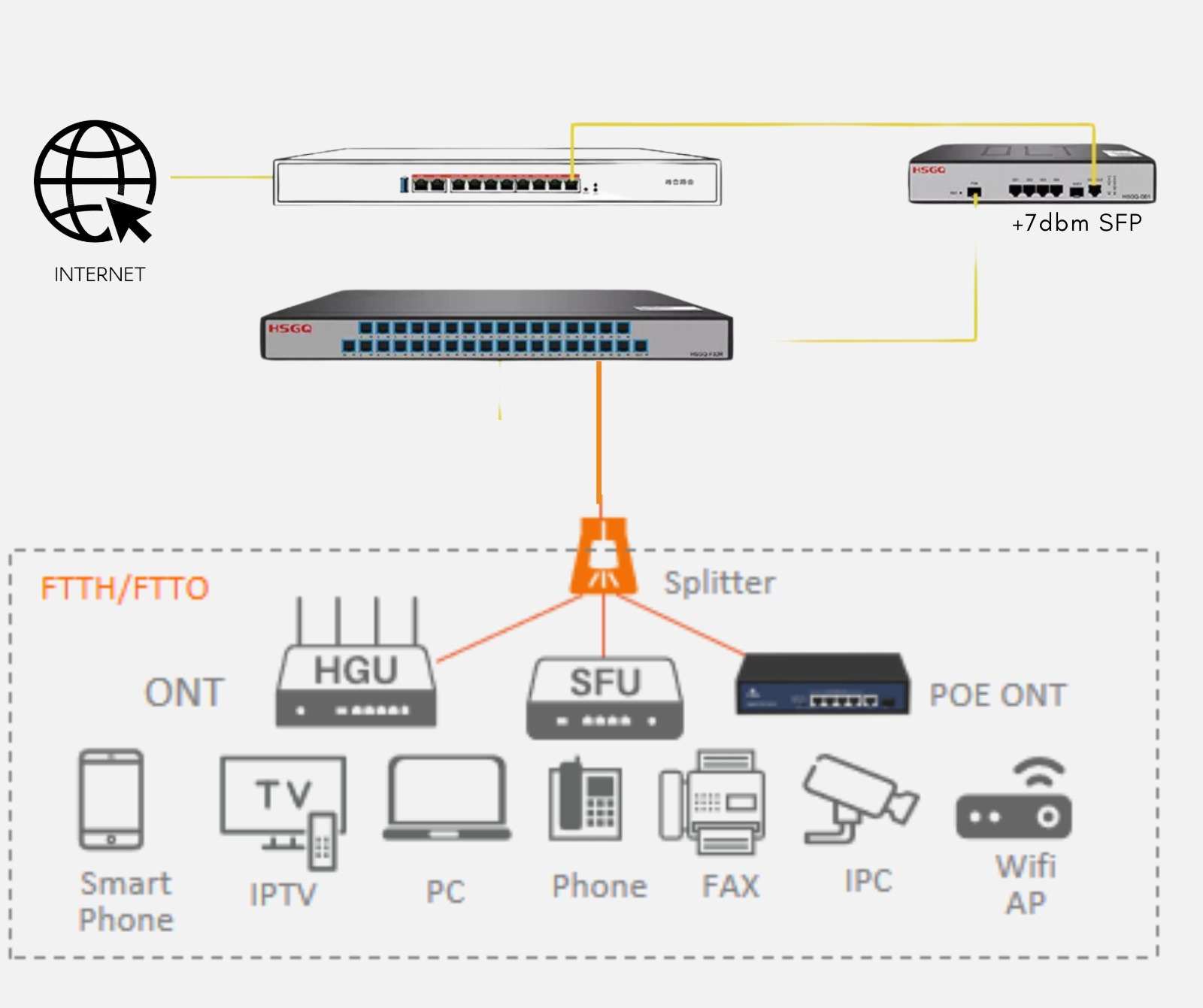
Core components of FTTH/FTTx
GPON network:
1.
Optical Line
Terminal (OLT): OLT is a component of
PON (Passive Optical Networks) used in fiber optic communication systems. Acts
as the central control unit in the GPON network, located at the service
provider's central office.
Functions:
ü Converts electrical signals to optical signals and
vice versa.
ü Manages bandwidth allocation and controls downstream
and upstream communication.
ü Support features like Dynamic Bandwidth Allocation (DBA) and Quality of Service (QoS)
2.
Optical
Distribution Frame (ODF): An
optical distribution frame (ODF) is a frame used to provide cable interconnections
between communication facilities, which can integrate fiber splicing, fiber
termination, fiber optic adapters & connectors and cable connections
together in a single unit. Serves
as a termination point for optical fibers, providing a platform for managing
and organizing fibers.
Functions:
ü Simplifies fiber connections and maintenance.
ü Provides protection to optical fibers against physical
damage.
ü Enables easy cross-connections and testing.

OLT (Optical line Terminal) Types:
EPON (Ethernet Passive Optical Network) and GPON (Gigabit Passive
Optical Network) are two key technologies used in fiber-optic networks for
broadband delivery, and both use Optical Line Terminals (OLTs)
to manage the communication between end-users (ONUs/ONTs) and the central
office or network. Each type of OLT has different port types that determine how
the device connects to users and handles data traffic.
1.
EPON OLT (Ethernet Passive Optical Network
OLT)
EPON is based on Ethernet standards and uses
optical fiber to connect users in a passive manner. The key feature of EPON is
that it uses Ethernet packets for data transmission, which simplifies the
integration of existing Ethernet networks and reduces costs.
Key
Features:
§ Protocol: Ethernet (IEEE 802.3ah
standard)
§ Speed: Typically 1 Gbps for both
downstream and upstream, though there are newer versions that can support up to
10 Gbps.
§ Architecture: Uses a shared medium
(optical splitters) to deliver data to multiple users.
§ Efficient for Data: Best for environments
where Ethernet is widely used and is ideal for data-intensive applications.
§
Deployment: Typically used for business and enterprise
networks where Ethernet-based services are prioritized.
Port types in EPON OLT:
1-Port
EPON OLT
§ Description: A 1-port EPON OLT
has one port for connecting to the optical network, allowing it to manage one
PON (Passive Optical Network). This configuration is typically used for
small-scale applications or trials.
§ Use Case: Suitable for testing,
small residential buildings, or pilot deployments.
§ Connector: SC/APC or LC/APC
connectors.
2-Port
EPON OLT
§ Description: A 2-port EPON OLT has two ports for connecting to two
separate optical networks, each managing a PON.
§ Use Case: This configuration is used for small businesses or
low-density residential deployments where a small number of users need to be
served.
§ Connector: SC/APC or LC/APC connectors.
8-Port
EPON OLT
§ Description: The 8-port configuration provides eight separate PON
ports, allowing the OLT to manage multiple optical networks and serve more
end-users.
§ Use Case: This configuration is often used for small residential
areas or businesses where the network needs to support a larger number of
customers. Each port typically serves 32-64 users, depending on the network
design.
§ Connector: SC/APC or LC/APC connectors.
16-Port
EPON OLT
§ Description: A 16-port EPON OLT offers 16 PON ports, increasing the
scalability of the network. This configuration is typically used in larger
deployments where the OLT needs to serve a high number of users (up to several
hundred).
§ Use Case: Used in large residential complexes or
small-medium-sized businesses where greater user density is expected.
§ Connector: SC/APC or LC/APC connectors.
32-Port
and Higher EPON OLTs
§ Description: High-port-count EPON OLTs can have even more ports
(e.g., 32, 64, or more) to meet the demand for larger-scale deployments.
§ Use Case: These are used in medium-to-large-scale service
provider networks and high-density residential buildings. The OLTs can support
thousands of users in large metropolitan areas or office buildings.
§ Connector: SC/APC or LC/APC connectors.
2.
GPON OLT (Gigabit Passive Optical Network OLT)
GPON is a more widely adopted PON technology,
offering higher speeds and more efficient bandwidth usage compared to EPON.
GPON OLTs are commonly used for FTTH (Fiber to the Home) and other broadband
services due to their higher performance.
Key Features:
§ Protocol: GPON (ITU-T G.984 standard)
§ Speed: 2.488 Gbps downstream, 1.244 Gbps upstream.
§ Efficient Bandwidth: GPON offers more efficient bandwidth allocation and
supports more services (voice, video, and data) with better QoS (Quality of
Service) management compared to EPON.
§ Higher Capacity: Supports more users per OLT compared to EPON, making it
more suitable for residential applications.
§ Deployment: GPON is mainly used for FTTH, FTTC (Fiber to the Curb),
and other fiber-based broadband deployments.
Port types in GPON
OLT
1-Port
GPON OLT
§ Description: A 1-port GPON OLT is configured
with a single PON port to serve a small number of users. The port typically
connects to an optical splitter, which then divides the signal among several
customers (up to 128 users depending on the splitter).
§ Use Case: Suitable for low-density
applications or pilot tests.
§ Connector: SC/APC or LC/APC
connectors for fiber-optic connections.
2-Port
GPON OLT
§ Description: The 2-port GPON OLT has
two PON ports, doubling the capacity and offering redundancy or serving two
separate geographical areas.
§ Use Case: This configuration might
be used in smaller residential communities, remote offices, or for redundancy
purposes.
§ Connector: SC/APC or LC/APC
connectors.
8-Port
GPON OLT
§ Description: An 8-port GPON OLT offers
8 independent PON ports. Each port connects to a separate optical splitter and
serves up to 128 customers. This configuration is ideal for low- to mid-sized
FTTH (Fiber to the Home) deployments.
§ Use Case: Typically used in
residential communities, apartment buildings, or business parks with a moderate
number of users.
§ Connector: SC/APC or LC/APC
connectors.
16-Port
GPON OLT
§ Description: A 16-port GPON OLT has 16
PON ports, allowing it to serve a higher number of users. Each port typically
handles up to 128 subscribers, so a 16-port OLT can serve 2,048 customers.
§
Our Partners







Secure Payment By

